Mouse Anti-Human CD56-BIOT (MEM 188)
Cat. No.:
9456-08
Biotin Anti-Human CD56 antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry / immunocytochemistry, and separation assays.
$206.00
| Clone | MEM 188 |
|---|---|
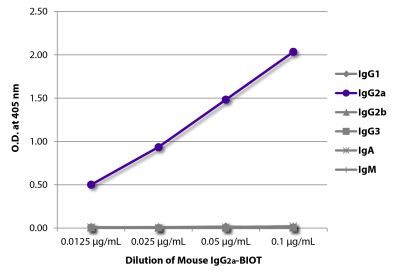
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2aκ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgG2a-BIOT (HOPC-1) |
| Specificity | Human/Porcine CD56 |
| Alternative Names | NCAM, neural cell adhesion molecule, Leu-19, NKH1 |
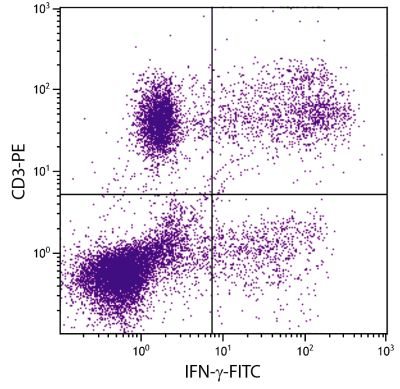
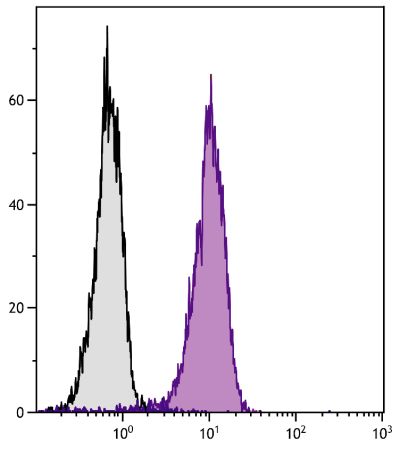
| Description | CD56, an isoform of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), is a heavily glycosylated type I transmembrane protein. On human hematopoietic cells its expression is restricted to NK cells and a subpopulation of T lymphocytes (known as large granular lymphocytes) which demonstrate natural killer activity. While it is clear that NCAM plays a role in homotypic adhesion of neuronal cells, the significance of CD56 expression on NK cells is not clear and remains controversial. |
| Immunogen | Acute myelogenous leukemia cell line KG-1 |
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | Lot specific |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
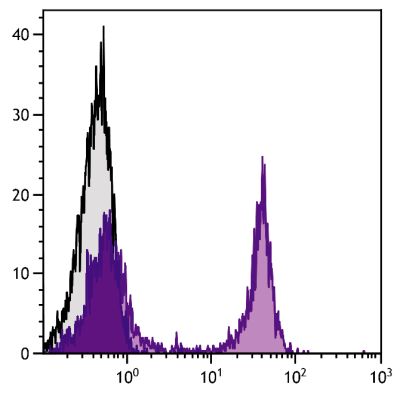
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,6-9 Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections – Reported in literature 1 Immunocytochemistry – Reported in literature 2 Separation – Reported in literature 3,4 Blocking – Reported in literature 5 |
| RRID Number | AB_2796804 |
| Gene ID |
4684 (Human) 100515564 (Porcine) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
NCAM1 (Human) NCAM1 (Porcine) |
| Gene ID Aliases | CD56; MSK39; NCAM |
| UniProt ID |
P13591 (Human) |
| UniProt Name |
NCAM1_HUMAN (Human) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Zahn S, Rehkämper C, Ferring-Schmitt S, Bieber T, Tüting T, Wenzel J. Interferon-α stimulates TRAIL expression in human keratinocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for the pathogenesis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165:1118-23. (IHC-FS, FC)
- 2. Hanabuchi S, Watanabe N, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ito T, Shaw J, et al. Human plasmacytoid predendritic cells activate NK cells through glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-ligand (GITRL). Blood. 2006;107:3617-23. (ICC)
- 3. Berney SM, Schaan T, Alexander JS, Peterman G, Hoffman PA, Wolf RE, et al. ICAM-3 (CD50) cross-linking augments signaling in CD3-activated peripheral human T lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:867-74. (Sep)
- 4. Liao, J, Huang M, Fast K, Gundling K, Yadav M, van Brocklyn JR, et al. Immunosuppressive human anti-lymphocyte autoantibodies specific for the type 1 sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. FASEB J. 2009;23:1786-96. (Sep)
- 5. Kos FJ, Chin CS. Costimulation of T cell receptor-triggered IL-2 production by Jurkat T cells via fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 upon its engagement by CD56. Immunol Cell Biol. 2002;80:364-9. (Block)
- 6. Hanna J, Mussaffi H, Steuer G, Hanna S, Deeb M, Blau H, et al. Functional aberrant expression of CCR2 receptor on chronically activated NK cells in patients with TAP-2 deficiency. Blood. 2005;106:3465-73. (FC)
- 7. Olsen I, Tollefsen S, Aagaard C, Reitan LJ, Bannantine JP, Andersen P, et al. Isolation of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis reactive CD4 T cells from intestinal biopsies of Crohn's disease patients. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5641. (FC)
- 8. Dimova T, Mihaylova A, Spassova P, Georgieva R. Superficial implantation in pigs is associated with decreased numbers and redistribution of endometrial NK-cell populations. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008;59:359-69. (FC, Porcine Reactivity)
- 9. Wilschut KJ, Jaksani S, Van Den Dolder J, Haagsman HP, Roelen BA. Isolation and characterization of porcine adult muscle-derived progenitor cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105:1228-39. (FC, Porcine Reactivity)
See More