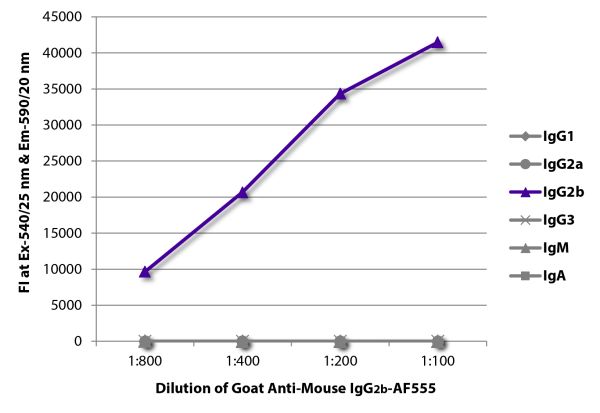
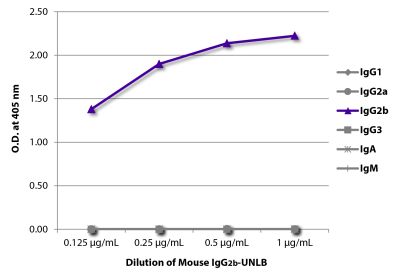
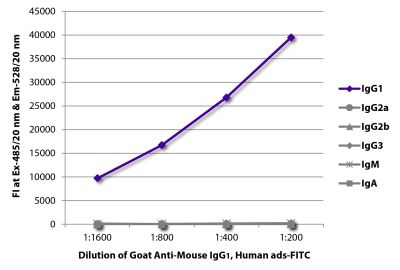
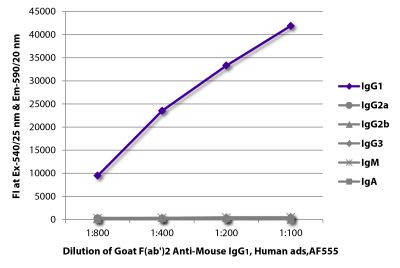
Goat Anti-Mouse IgG2b-AF555
Cat. No.:
1091-32
Goat Anti-Mouse IgG2b-Alexa Fluor® 555 antibody for use in fluorescent assays.
$262.00

| Isotype | Goat IgG |
|---|---|
| Isotype Control | 0109-32 |
| Specificity | Reacts with the heavy chain of mouse IgG2b |
| Source | Pooled antisera from goats hyperimmunized with mouse IgG2b |
| Cross Adsorption | Mouse IgG1, IgG2a, IgG3, IgM, and IgA; may react with immunoglobulins from other species |
| Purification Method | Affinity chromatography on mouse IgG2b covalently linked to agarose |
| Conjugate | AF555 (Alexa Fluor® 555) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C; Avoid exposure to light |
| Trademark Information | Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. or its subsidiaries |
| Applications |
Quality tested applications for relevant formats include - ELISA 1 FLISA |
| RRID Number | AB_2794545 |
| Gene ID |
16016 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Ighg2b (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | IgG2b; Igh-3; gamma2b |
| UniProt ID |
P01867 (Mouse) |
| UniProt Name |
IGG2B_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
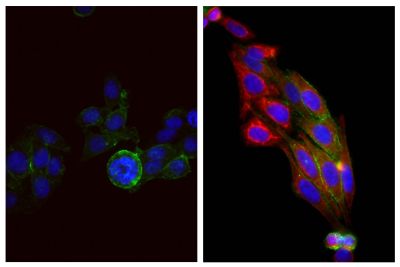
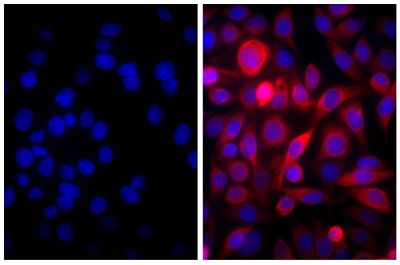
- 1. Silva-Sanchez A, Liu CR, Vale AM, Khass M, Kapoor P, Elgavish A, et al. Violation of an evolutionarily conserved immunoglobulin diversity gene sequence preference promotes production of dsDNA-specific IgG antibodies. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0118171. (ELISA)


![Wdpks1Δ-1 yeast cells treated with liquid nitrogen were stained with anti-melanin followed by Goat Anti-Mouse IgM, Human ads-TRITC (SB Cat. No. 1020-03).<br/>Image from Paolo WF Jr, Dadachova E, Mandal P, Casadevall A, Szaniszlo PJ, Nosanchuk JD. Effects of disrupting the polyketide synthase gene <i>WdPKS1</i> in <i>Wangiella</i> [<i>Exophiala</i>] <i>dermatitidis</i> on melanin production and resistance to killing by antifungal compounds, enzymatic degradation, and extremes in temperature. BMC Microbiol. 2006;6:55. Figure 5(d)<br/>Reproduced under the Creative Commons license https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://www.southernbiotech.com/media/catalog/product/cache/3409635b2d8a6f8a49dab513db4d1386/e/1/e1bdcbb171112075fbda9bda20f45e7e878c207c8caf1773ba0e0bf58185d151.jpeg)