Mouse Anti-Mouse Ly-49F-UNLB (HBF-719)
Cat. No.:
1803-01
Purified Anti-Mouse Ly-49F antibody for use in flow cytometry assays.
$319.00
| Clone | HBF-719 |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Mouse (BALB/c) IgG1κ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgG1-UNLB (15H6) |
| Specificity | Mouse Ly-49F |
| Alternative Names | Ly-49 |
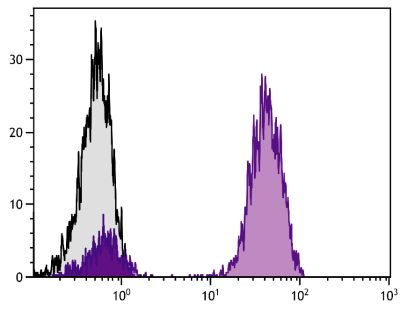
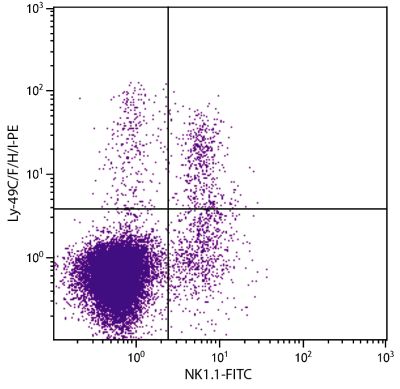
| Description | The monoclonal antibody HBF-719 reacts with the B6 allele of Ly49F, a member of the lectin-like homodimeric Ly49 family of cell surface receptors. Mouse Ly49 receptors exhibit allelic specificity for MHC class I Ia molecules and are thought to serve to prevent natural killer (NK) cells from attacking normal cells while allowing them to attack infected or transformed cells in which class I molecules have been downregulated. These inhibitory receptors are also expressed on subpopulations of mouse CD8+ T cells. The HBF-719 antibody stains ~11% of NK1.1+CD3- splenocytes, and 3.5% (2.5 month old) to 10.0% (11 month old) of CD8+ spleen cells from C57BL/6 mice. |
| Immunogen | CHO-K1 cells transfected with B6 allele of Ly49F gene |
| Conjugate | UNLB (Unconjugated) |
| Buffer Formulation | Borate buffered saline, pH 8.2 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,2 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795335 |
| Gene ID |
16637 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Klra6 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | Ly49f; ly-49f |
| UniProt ID |
Q60653 (Mouse) |
| UniProt Name |
KLRA6_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Coles MC, McMahon CW, Takizawa H, Raulet DH. Memory CD8 T lymphocytes express inhibitory MHC-specific Ly49 receptors. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:236-44. (Immunogen, FC)
- 2. Denning TL, Granger S, Mucida D, Graddy R, Leclercq G, Zhang W, et al. Mouse TCRαβ+CD8αα intraepithelial lymphocytes express genes that down-regulate their antigen reactivity and suppress immune responses. J Immunol. 2007;178:4230-9. (FC)