Mouse Anti-Chicken MHC Class I-BIOT (F21-2)
Cat. No.:
8345-08
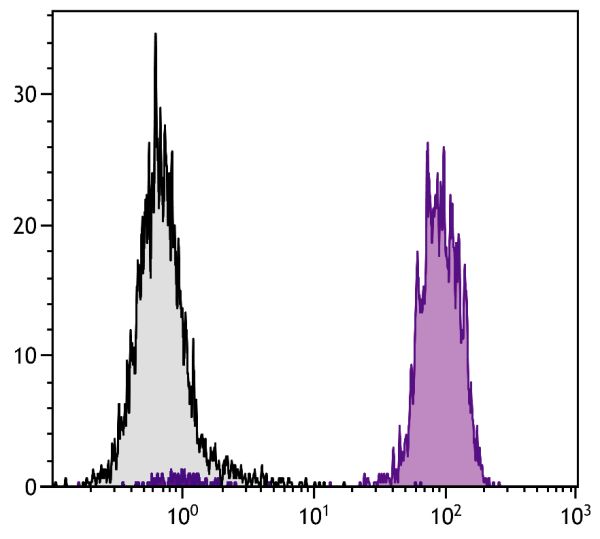
Biotin Anti-Chicken MHC Class I antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, western blot, and immunoprecipitation assays.
$353.00
| Clone | F21-2 |
|---|---|
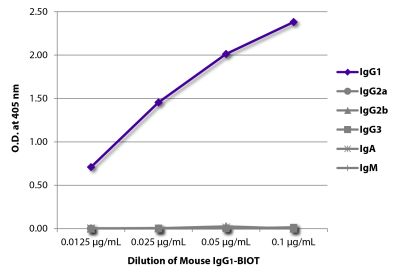
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1κ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgG1-BIOT (15H6) |
| Specificity | Chicken/Turkey MHC Class I |
| Alternative Names | B-F |
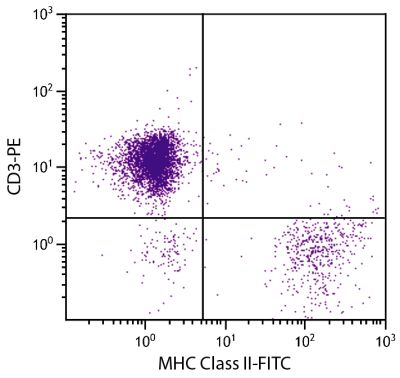
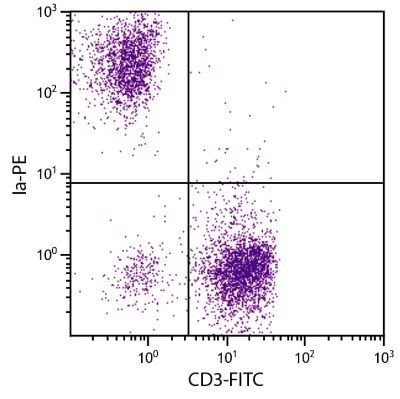
| Description | Like their mammalian counterparts, avian MHC Class I molecules, also known as B-F antigens, consist of a highly polymorphic α-chain noncovalently bound to the invariant β2-microglobulin subunit. MHC Class I molecules are expressed on most nucleated cells where they present endogenously synthesized antigenic peptides to CD8+ T lymphocytes, which are usually cytotoxic T cells. The monoclonal antibody F21-2 also reacts with turkey MHC Class I. |
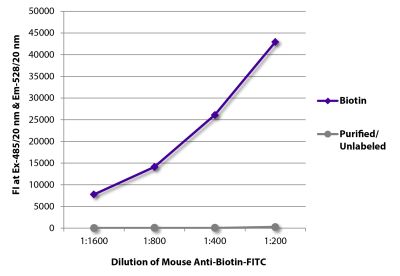
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
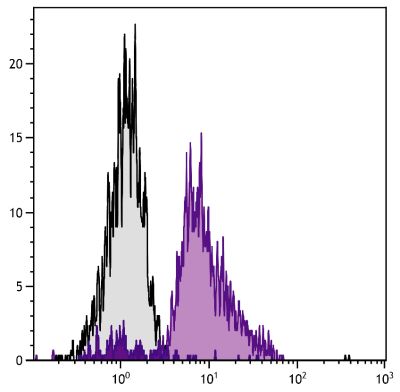
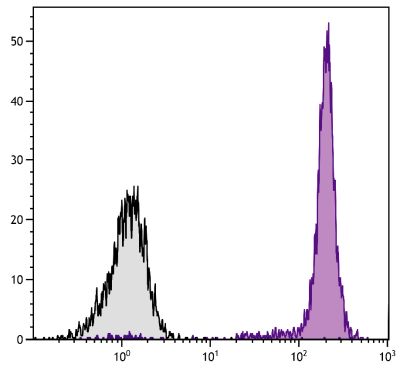
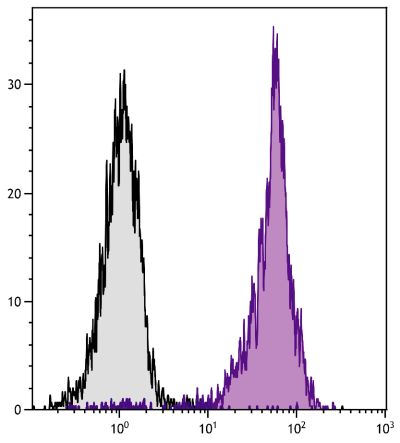
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 3,8-12 Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections – Reported in literature 3,4 Electron Microscopy – Reported in literature 13 Immunoprecipitation – Reported in literature 1,2,5 Western Blot – Reported in literature 1,2 Purification – Reported in literature 1,2,6 Blocking – Reported in literature 7 |
| RRID Number | AB_2796510 |
| Gene ID |
693260 (Chicken) 425389 (Chicken) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
BF1 (Chicken) BF2 (Chicken) |
| Gene ID Aliases | B-F; B-F-S04; B-F-S05; B-F-S06; B-F-S07; B-F1; B-FI; B-FIV; BF; BF2; BFa2; BFw-03; BFw-05; BFz-01; HFE; B-F-S01; B-F-S02; B-F-S03; B-F-S09; B-F-S11; B-F-S12; B-F-S13; B-F-S14; B-LB2; B12; BF12; BFIV; BFIV21; BFa1 |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Salomonsen J, Skjødt K, Crone M, Simonsen M. The chicken erythrocyte-specific MHC antigen. Characterization and purification of the B-G antigen by monoclonal antibodies. Immunogenetics. 1987;25:373-82. (IP, WB, Purification)
- 2. Møller LB, Kaufman J, Verland S, Salomonsen J, Avila D, Lambris JD, et al. Variations in the cytoplasmic region account for the heterogeneity of the chicken MHC class I (B-F) molecules. Immunogenetics. 1991;34:110-20. (IP, WB, Purification)
- 3. Dunon D, Salomonsen J, Skjødt K, Kaufman J, Imhof BA. Ontogenic appearance of MHC class I (B-F) antigens during chicken embryogenesis. Dev Immunol. 1990;1:127-35. (IHC-FS, FC)
- 4. Subedi K, Yoshimura Y. Expression of MHC class I and II in growing ovarian follicles of young and old laying hens, Gallus domesticus. J Poult Sci. 2005;42:101-9. (IHC-FS)
- 5. Dunon D, Kaufman J, Salomonsen J, Skjoedt K, Vainio O, Thiery J, et al. T cell precursor migration towards β2-microglobulin is involved in thymus colonization of chicken embryos. EMBO J. 1990;9:3315-22. (IP, IHC-FS)
- 6. Wallny H, Avila D, Hunt LG, Powell TJ, Riegert P, Salomonsen J, et al. Peptide motifs of the single dominantly expressed class I molecule explain the striking MHC-determined response to Rous sarcoma virus in chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:1434-9. (Purification)
- 7. Haghighi HR, Read LR, Haeryfar SM, Behboudi S, Sharif S. Identification of a dual-specific T cell epitope of the hemagglutinin antigen of an h5 avian influenza virus in chickens. PLoS One. 2009;4(11):e7772. (Block)
- 8. Del Cacho E, Gallego M, Lillehoj HS, López-Bernard F, Sánchez-Acedo C. Avian follicular and interdigitating dendritic cells: isolation and morphologic, phenotypic, and functional analyses. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009;129:66-75. (FC)
- 9. Singh S, Briles WE, Lupiani B, Collisson EW. Avian influenza viral nucleocapsid and hemagglutinin proteins induce chicken CD8+ memory T lymphocytes. Virology. 2010;399:231-8. (FC)
- 10. Sunkara LT, Achanta M, Schreiber NB, Bommineni YR, Dai G, Jiang W, et al. Butyrate enhances disease resistance of chickens by inducing antimicrobial host defense peptide gene expression. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27225. (FC)
- 11. Verweij MC, Lipińska AD, Koppers-Lalic D, van Leeuwen WF, Cohen JI, Kinchington PR, et al. The capacity of UL49.5 proteins to inhibit TAP is widely distributed among members of the genus Varicellovirus. J Virol. 2011;85:2351-63. (FC)
- 12. Meyerhoff RR, Ali RA, Liu K, Huang G, Koci MD. Comprehensive analysis of commercially available mouse antichicken monoclonal antibodies for cross-reactivity with peripheral blood leukocytes from commercial turkeys. Poult Sci. 2012;91:383-92. (FC, Turkey Reactivity)
- 13. del Cacho E, Gallego M, Lee SH, Lillehoj HS, Quilez J, Lillehoj EP, et al. Induction of protective immunity against Eimeria tenella infection using antigen-loaded dendritic cells (DC) and DC-derived exosomes. Vaccine. 2011;29:3818-25. (EM)
See More