Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b-BIOT (DX5)
Cat. No.:
1806-08
Biotin Anti-Mouse CD49b antibody for use in flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry assays.
$261.00

| Clone | DX5 |
|---|---|
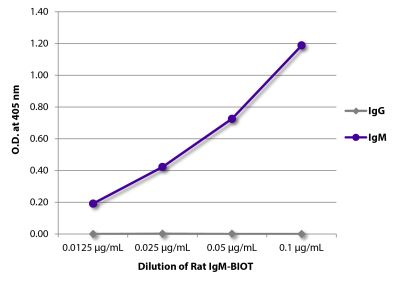
| Isotype | Rat (Lewis) IgMκ |
| Isotype Control | Rat IgM-BIOT (NIP/M-2) |
| Specificity | Mouse CD49b |
| Alternative Names | α2 integrin, VLA-2α, very late antigen-2, pan NK |
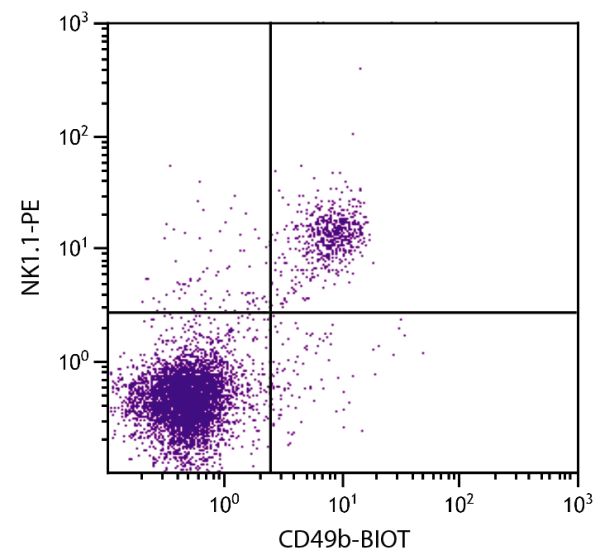
| Description | The monoclonal antibody DX5 reacts with CD49b, also known as very late antigen-2 (VLA-2) and α2 integrin. The antibody stains the majority of NK cells and a small subpopulation of T cells in all mouse strains tested (e.g., A/J, AKR, BALB/c, C3H/HeJ, C57BL/6, C57BL/10, C57BR, C58, CBA/Ca, CBA/J, DBA/1, DBA/2, SJL, SWR). Three-color flow cytometry analysis has revealed that most cells that express NK-1.1 (NKR-P1C) also express CD49b. However, small subsets of DX5+NK-1.1- and DX5-NK-1.1+ cells can be found, especially among the CD3+ population of T lymphocytes. NK cells cultured in the presence of IL-2 progressively lose reactivity with DX5 as a consequence of cellular proliferation. Therefore, DX5 can be used to define functionally distinct subsets of murine NK cells. The monoclonal antibody DX5 has not been demonstrated to have activating or blocking activity. |
| Immunogen | NK cells isolated from C57BL/6 mice |
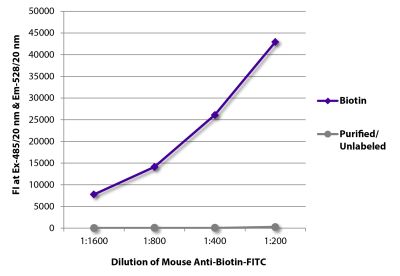
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
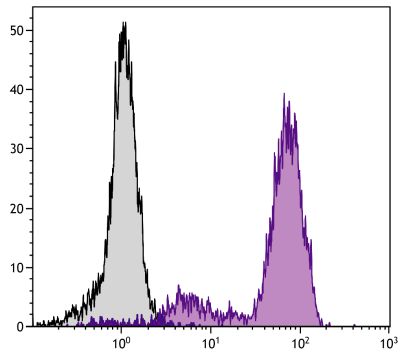
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,4-8 Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin Sections – Reported in literature 2 Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections – Reported in literature 3 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795358 |
| Gene ID |
16398 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Itga2 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | CD49B; DX5; GPIa |
| UniProt ID |
Q62469 (Mouse) |
| UniProt Name |
ITA2_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Arase H, Saito T, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Cutting edge: the mouse NK cell-associated antigen recognized by DX5 monoclonal antibody is CD49b (α2 integrin, very late antigen-2). J Immunol. 2001;167:1141-4. (Immunogen, FC)
- 2. Oertelt S, Lian Z, Cheng C, Chuang Y, Padgett KA, He X, et al. Anti-mitochondrial antibodies and primary biliary cirrhosis in TGF-β receptor II dominant-negative mice. J Immunol. 2006;177:1655-60. (IHC-PS)
- 3. de Vries MR, Seghers L, van Bergen J, Peters HA, de Jong RC, Hamming JF, et al. C57BL/6 NK cell gene complex is crucially involved in vascular remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;64:51-8. (IHC-FS)
- 4. Pan P, Gu P, Li Q, Xu D, Weber K, Chen S. Regulation of dendritic cell function by NK cells: mechanisms underlying the synergism in the combination therapy of IL-12 and 4-1BB activation. J Immunol. 2004;172:4779-89. (FC)
- 5. López MC, Duckett NS, Baron SD, Metzger DW. Early activation of NK cells after lung infection with the intracellular bacterium, Francisella tularensis LVS. Cell Immunol. 2004;232:75-85. (FC)
- 6. Lin Y, Zhong Y, Saito S, Chen Y, Shen W, Di J, et al. Characterization of natural killer cells in nonobese diabetic/severely compromised immunodeficient mice during pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:2676-86. (FC)
- 7. Adhikari AS, Agarwal N, Wood BM, Porretta C, Ruiz B, Pochampally RR, et al. CD117 and Stro-1 identify osteosarcoma tumor-initiating cells associated with metastasis and drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2010;70:4602-12. (FC)
- 8. Bartemes KR, Iijima K, Kobayashi T, Kephart GM, McKenzie AN, Kita H. IL-33-responsive lineage- CD25+ CD44hi lymphoid cells mediate innate type-2 immunity and allergic inflammation in the lungs. J Immunol. 2012;188:1503-13. (FC)
See More